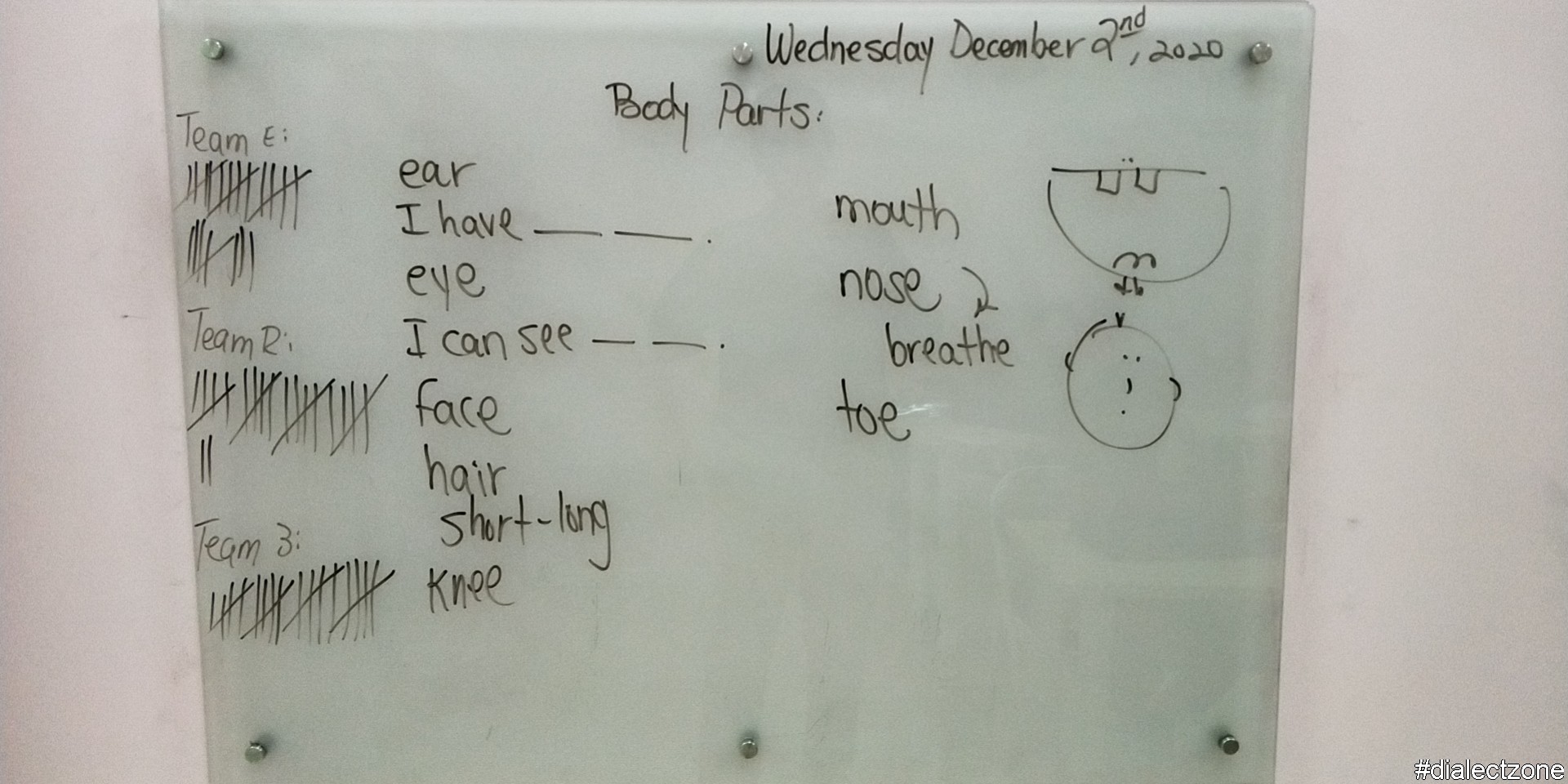
Ear: ear – [eer] – /ɪər/
Eye: eye – [ahy] – /aɪ/
Face: face – [feys] – /feɪs/
Hair: hair – [hair] – /hɛər/
Knee: knee – [nee] – /ni/
Mouth: mouth – [noun mouth; verb mouth] – /noun maʊθ; verb maʊð/
Nose: nose – [nohz] – /noʊz/
Toes: toe – [toh] – /toʊ/


The human body is the structure of a human being. It is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organ systems. They ensure homeostasis and the viability of the human body.
It comprises a head, neck, trunk (which includes the thorax and abdomen), arms and hands, legs and feet.
The study of the human body involves anatomy, physiology, histology and embryology. The body varies anatomically in known ways. Physiology focuses on the systems and organs of the human body and their functions. Many systems and mechanisms interact in order to maintain homeostasis, with safe levels of substances such as sugar and oxygen in the blood.
The body is studied by health professionals, physiologists, anatomists, and by artists to assist them in their work.
Major Human Body Systems
- Circulatory System: Pumps and channels blood to and from the body and lungs, plays an important role in the transportation of nutrients, gases, hormones and wastes through the body. It consists of heart, blood and blood vessels.
- Digestive System: Digests and processes the ingested food. It is involved in the breakdown and absorption of nutrients and it promotes growth and maintenance. It consists of salivary glands, esophagus, stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, intestines, rectum, and anus.
- Endocannabinoid System: Consists of neuromodulatory lipids and receptors which help in a variety of physiological processes including appetite, pain-sensation, mood, motor learning, synaptic plasticity, and memory.
- Endocrine System: Communicates within the body using hormones made by endocrine glands like the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, pineal gland, thyroid, parathyroid and adrenal glands. Hormones control the physiological processes in the body and psychological behavior of the person.
- Integumentary System: Consists of skin, hair, and nails.
- Immune System: Fights off diseases, consists of leukocytes, tonsils, adenoids, thymus, and spleen.
- Lymphatic System: Transfers lymph between tissues and the bloodstream, consists of the lymph and lymph nodes and vessels that transport it.
- Musculoskeletal System: Helps move the body with muscles and tendons. Movement of the muscles promotes movement of fluids, food or blood (for example, in the stomach, intestines, and heart). It consists of both skeletal and smooth muscles.
- Nervous System: Gathering, processing and transferring information to and from the body with the brain, spinal cord, and the nerves.
- Reproductive System: Female reproductive system consists of ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, mammary glands, and the male reproductive system consists of testes, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate, and penis.
- Respiratory System: Breathing system that helps absorb oxygen from the air and expel carbon dioxide from the body. It consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs, and diaphragm.
- Skeletal System: Gives shape to the body and holds the body. It protects the delicate organs. It consists of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons.
- Urinary System: Maintains fluid balance, electrolyte balance and administers excretion of urine. It helps get rid of the cellular wastes, toxins, excess water or nutrients from the circulatory system. It consists of kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
- Vestibular System: It helps maintain the balance of the body and the sense of spatial orientation.
Human Body
Let us now divide the body into different regions; so that it will be easier to make a body parts list.
Regional Parts
- Head and Neck: The upper region of the body includes everything above the neck, for instance, hair, scalp, eyes, ears, nose, mouth, tongue, teeth, etc.
- Upper Limb: This region includes the shoulder, arm, hand, wrist, forearm, elbow and fingers.
- Thorax: This is the region of the chest from the thoracic inlet to the thoracic diaphragm.
- Middle Region: This includes human abdomen to the pelvic brim or to the pelvic inlet.
- Back Region: The region includes the spine and its components, the vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx, and intervertebral discs.
- Pelvic Region: This region includes the pelvis which consists of everything from the pelvic inlet to the pelvic diaphragm. The perineum is the region that consists of the sex organs and the anus.
- Lower Limb Region: This includes everything below the inguinal ligament, including the hip, the thigh, the knee, the leg, the ankle and the foot.
Internal Parts
For the sake of convenience, you may divide body organs into ‘Organs on the left side of the body’ and ‘Organs on the right side of the human body’. Here is a list of the main internal organs of the human body.
- Adrenals
- Appendix
- Bladder
- Brain
- Esophagus
- Eyes
- Gallbladder
- Heart
- Intestines
- Kidney
- Liver
- Lung
- Ovaries
- Pancreas
- Parathyroids
- Pituitary
- Prostate
- Spleen
- Stomach
- Testicles
- Thymus
- Thyroid
- Uterus
- Veins
It is just impossible to mention all the organs, here. Almost every organ is made up of various parts which can also be named separately as organs. For example, the brain consists of Amygdala, Brainstem, Cerebellum, Cerebral cortex, Limbic system, Medulla, Midbrain, and Pons. There are specific names for the nerves, muscles, bones, tendons etc. which are present at the given specific locations. For instance, Achilles tendon, Bachmann’s bundle, Ducts of Bellini, Darwin’s tubercle, etc.
External Parts
- Head
- Forehead
- Jaw
- Cheek
- Chin
- Eye
- Ear
- Nose
- Mouth
- Teeth
- Tongue
- Throat
- Neck
- Adam’s apple
- Shoulders
- Arm
- Elbow
- Wrist
- Hand
- Fingers
- Thumb
- Spine
- Chest
- Thorax
- Breast
- Abdomen
- Groin
- Hip
- Buttocks
- Navel
- Penis
- Scrotum
- Clitoris
- Vulva
- Leg
- Thigh
- Knee
- Calf
- Heel
- Ankle
- Foot
- Toes
Anatomical charts and models of bodily systems help study human physiology. The human body, a scientific marvel has always been an interesting topic for various researches related to body mechanisms like aging, fighting diseases, the effect of stress on health, etc.